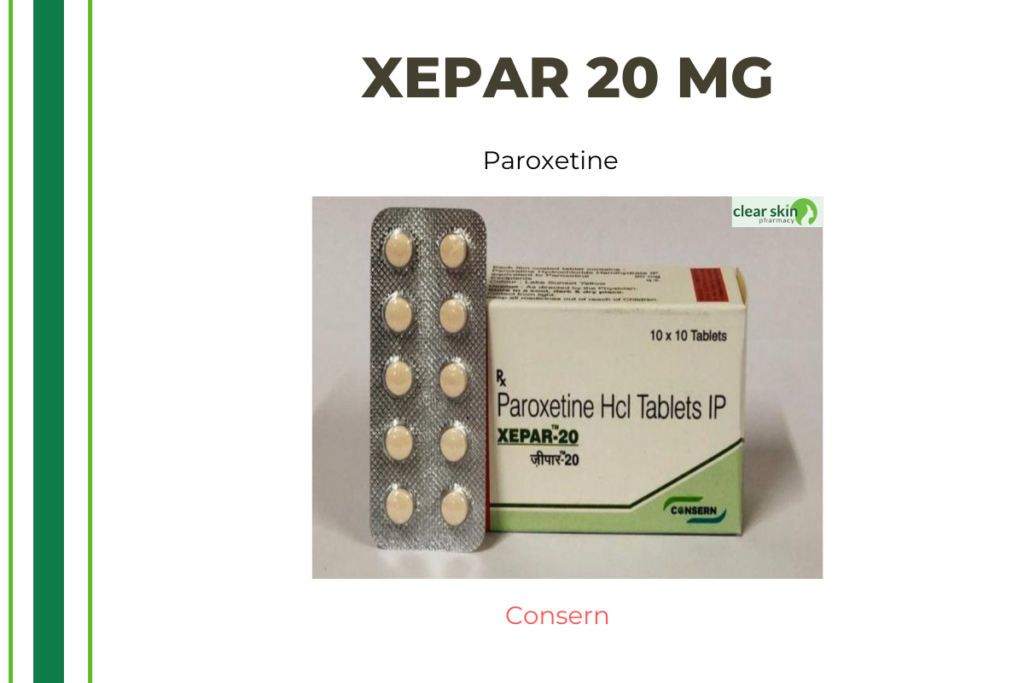
Xepar
Antidepressant medication XEPAR is used for the treatment of severe depression, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, premenstrual dysphoria disorder, and generalized anxiety disorder. Depression is a mood disorder marked by sorrow, unhappiness, anger, hopelessness, or loss that interferes with daily tasks.
Paroxetine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, is included in XEPAR. It functions by blocking the reuptake of serotonin in the brain, which is a mood-boosting chemical messenger between brain cells. By raising serotonin concentrations in the neural synapse, this helps regulate mood and heal depression and anxiety disorders.
Take XEPAR precisely as prescribed. Depending on your medical condition and reaction to therapy, you should continue taking XEPAR for as long as your doctor has instructed. Certain common side effects may occur, including insomnia (difficulty sleeping), dizziness, headache, diarrhea, nausea, tiredness, dry mouth, appetite loss, pin and sexual dysfunction. If you are having these side effects frequently, you should visit a physician.
Avoid using XEPAR if you are pregnant, since it may damage the fetus. Before using XEPAR if you are nursing, talk to your doctor. While using XEPAR, you may have dizziness, disorientation, fatigue, and decreased eyesight; thus, you should not drive or operate heavy machinery. Children under the age of 18 should not use XEPAR since its safety and efficacy have not been established. Alcohol should be avoided when using XEPAR, since it may worsen symptoms or harmful effects. To rule out any adverse effects, keep your doctor informed about your current health status and medications.
Xepar’s Applications
Major depressive disorders include OCD, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, and generalized anxiety disorder.
Medicinal Advantages
XEPAR is an antidepressant drug known as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor. XEPAR is effective for treating major depressive disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, premenstrual dysphoric disorder, and generalized anxiety disorder. XEPAR functions by blocking the reabsorption of serotonin, a mood-enhancing chemical messenger in the brain that communicates between brain cells, by nerves. By raising serotonin concentrations in the neural synapse, this helps regulate mood and heal depression and anxiety disorders. XEPAR aids in the recovery from depression and has less adverse effects than antidepressants of the past.
Use Instructions
To avoid stomach pain, take XEPAR with breakfast in the morning. Your physician will choose how long you should take XEPAR based on your medical condition and response to therapy. XEPAR should be taken precisely as prescribed by a physician. XEPAR is available in both tablet and liquid form. Tablet: Swallow one XEPAR tablet whole with a glass of water. Do not chew or crush the tablet. Use the measuring cup included in the packaging to measure the recommended dose; shake the container thoroughly before to use.
Storage
Place in a cool, dry area out of direct sunlight.
XEPAR Side Effects
Difficulty sleeping
Headache
Diarrhea
Nausea
Fatigue
Mouth is parched
Appetite loss.
Disturbances in sexual activity
Precautions and Warnings in Depth
Do not take PEXEP if you are allergic to any of its constituents, are taking or have recently taken monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI), or are taking antipsychotic drugs such as thioridazine or pimozide. Consult your physician immediately if you have suicidal thoughts, such as murdering or harming oneself. Inform your doctor if you have/have had epilepsy, mania, diabetes, low blood salt levels, glaucoma, or are getting electroconvulsive treatment for severe depression before using XEPAR. Avoid using XEPAR if you are pregnant, since it may damage the fetus. Before using XEPAR if you are nursing, talk to your doctor. While using XEPAR, you may have dizziness, disorientation, fatigue, and decreased eyesight; thus, you should not drive or operate heavy machinery. Children under the age of 18 should not use XEPAR since its safety and efficacy have not been established. Alcohol should be avoided when using XEPAR, since it may worsen symptoms or harmful effects.
Interactions Between Drugs
Interactions between drugs: Antipsychotics (perphenazine, thioridazine, clozapine) and blood thinners (warfarin, clopidogrel) may interact with PAROXETINE. NSAIDs (acetylsalicylic acid, ibuprofen, celecoxib, etodolac, diclofenac, meloxicam, tramadol, pethidine), antidepressants (clomipramine, moclobemide, methylthioninium chloride/methylene blue, nortriptyline, desipramine), anti-cancer (tamoxifen), anti-migraine (sum (Procyclidine).
Contraindications: Do not mix PAROXETINE with St. John’s wort (an herbal supplement used to treat depression). When alcohol is used with PAROXETINE, the sedative effects may be intensified.
Multiple disorders, including glaucoma, diabetes, epilepsy, mania, bleeding difficulties, hyponatremia (low salt levels), heart, liver, and kidney dysfunction, may interact with PAROXETINE.
Safety Suggestions
ALCOHOL
While using PAROXETINE, you should avoid consuming alcohol since it might worsen side effects and symptoms.
PREGNANCY
The drug PAROXETINE is designated as pregnancy category D. If you are pregnant or intending to get pregnant, you should avoid using PAROXETINE since it might be harmful to the fetus.
BREAST FEEDING
There is PAROXETINE in breast milk. Consult your physician before using PAROXETINE; your physician will assess if PAROXETINE is safe for nursing mothers.
DRIVING
PAROXETINE may cause vertigo, disorientation, fatigue, and blurred vision as adverse effects. If you experience these symptoms, you should not drive or operate heavy machinery.
LIVER
In individuals with liver illness, it may be required to alter the dosage. If you have any concerns about this or if you have a liver condition, please consult a physician.
KIDNEY
In individuals with renal problems, it may be required to alter the dosage. Please consult a physician if you have any concerns about this or if you have renal impairment.
No habit formation
Advice on Diet and Lifestyle
Maintaining a good diet and engaging in regular physical activity can aid in enhancing both overall health and self-esteem.
Frequent therapy sessions are required.
Engage in yoga and meditation. This reduces anxiety and calms the body.
To increase the quantity and quality of your sleep, maintain a consistent sleep routine.
Omega fatty acids may be found in abundance in fish, nuts, fresh fruits and vegetables, and olive oil.
Neurotransmitter building components are amino acids. Meat, dairy products, and some fruits and vegetables are rich in amino acids, which are necessary for the proper maintenance of neurotransmitters.
Complex carbohydrates activate serotonin (a feel-good neurotransmitter). They include whole grains, beans, spinach, broccoli, oranges, and pears.
Exercise stimulates the body’s production of natural antidepressants. Additionally, it benefits in stress reduction, mood improvement, self-esteem increase, and restful sleep.
Avoid tobacco use and alcohol consumption.
Learn about your disease, identify the risk factors, and adhere to your doctor’s treatment plan.
Recommendations
Patients using PAROXETINE for suicidal behavior should be followed regularly. Consult your doctor immediately if you are contemplating self-harm or suicide.
Additional Information: This item is non-refundable.
Glossary of Diseases and Conditions
Depressive sickness (major depressive disorder): Clinical depression, also known as major depressive disorder, is a mental health illness characterized by a prolonged and persistent state of extreme melancholy. Affects mood, behavior, and other physiologic systems like sleep and hunger. Symptoms include sadness, loss of interest, dietary changes, sleep disturbances, restlessness, fatigue, feelings of worthlessness or guilt, thoughts of self-harm, and difficulties focusing, making decisions, and thinking. The exact etiology of depression is unknown. However, stress, hormonal changes, alcohol or drug abuse, maltreatment in childhood, certain medical conditions, and medicines may all increase the likelihood of developing depression.
Obsessive-Compulsive Condition (OCD) is a mental disorder characterized by obsessive thoughts (obsessions) and the desire to do tasks repeatedly (compulsions). Symptoms include a fear of germs and an intense drive to organize everything in a certain way.
This anxiety condition is characterized by panic episodes. When a person is in this position, he or she experiences terror even in the absence of danger. Symptoms include a rapid heartbeat, trouble breathing, chest or stomach discomfort, weakness or vertigo, and profuse perspiration.
In social contexts, social anxiety disorder is characterized by acute dread, anxiety, embarrassment, and self-consciousness. Symptoms include excessive dread, worry about humiliation or embarrassment, concern about upsetting someone, and fear of being judged.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a condition characterized by an inability to recover following exposure to or experience of a stressful event. This condition can last for months or even years, with triggers reviving traumatic memories and eliciting intense physical and emotional responses. Symptoms include nightmares, flashbacks, anxiety or despair, a heightened reaction to stimuli, and avoiding situations that may cause trauma.
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is a mental health illness characterized by pervasive feelings of anxiety, worry, or dread that interfere with everyday functioning. Anxiety is a natural response of the body to stress, marked by intense and incapacitating fear. Depression is the most prevalent kind of emotional disorder, affecting people of all ages. Anxiety is characterized by rapid breathing, an increased heart rate, restlessness, trouble focusing, and difficulties falling asleep.
Premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) is a severe type of premenstrual syndrome marked by physical and behavioral symptoms that typically subside once the menstrual cycle begins. Extreme mood fluctuations caused by premenstrual dysphoric disorder can negatively impact relationships and the workplace. Among the symptoms include irritability, wrath, despair, sadness, bloating, and breast pain.
FAQs
PAROXETINE prevents nerves from reabsorbing serotonin, a mood-enhancing chemical messenger in the brain that communicates between brain cells. This contributes to the regulation of mood by raising serotonin levels in neural synapses.
PAROXETINE is utilized to treat Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), Panic Disorder, Social Anxiety Disorder, Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder, and Generalized Anxiety Disorder.
If you discontinue PAROXETINE without seeing a physician, you may have withdrawal symptoms. Continue taking PAROXETINE for as long as prescribed to treat your condition successfully. If you have any issues while taking PAROXETINE, do not hesitate to inform your physician; the dosage may be gradually decreased.
It is possible for PAROXETINE to cause a decline in libido (sexual desire), impotence (erectile dysfunction), abnormal ejaculation, and orgasm problems. If you have any concerns, see your physician.
Dry mouth is a potential adverse effect of PAROXETINE. Reducing caffeine intake, avoiding smoking and mouthwashes containing alcohol, drinking water often, and chewing sugar-free gum/candy may boost saliva production and prevent tongue dryness.
Consult your physician before using PAROXETINE if you have glaucoma, since it may raise intraocular pressure.
Consult your physician before using PAROXETINE if you have diabetes, since it may affect blood glucose levels. If you are using PAROXETINE, you should regularly monitor your blood sugar levels. Consult a doctor if your blood sugar levels are fluctuating.
People who take antidepressants such as PAROXETINE are more prone to have suicidal ideation. Consult your doctor immediately if you are contemplating self-harm or suicide.
Consult your physician before using tamoxifen (a cancer therapy) with PAROXETINE. PAROXETINE may reduce the effectiveness of tamoxifen.
Taking PAROXETINE may result in unexpected bleeding or bruising, such as blood in the vomit or feces. Consult your doctor before using PAROXETINE if you have a history of bleeding problems or are taking drugs that may increase the risk of bleeding, such as blood thinners (warfarin), antipsychotics (perphenazine or clozapine), tricyclic antidepressants (clomipramine), or NSAIDs (acetylsalicylic acid, ibuprofen, celecoxib, etodolac, diclofenac, meloxicam).



Be the first to review “XEPAR 20MG 10 tablets”