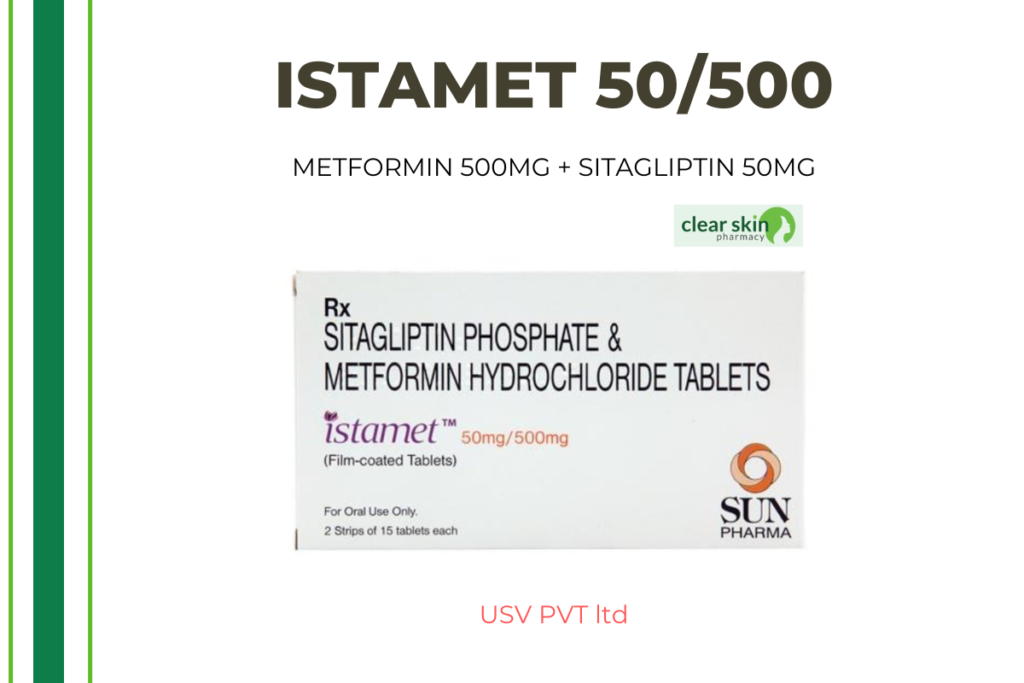
Istamet 50 mg/500 mg
The combination drug Istamet 50 mg/500 mg contains Sitagliptin (a DPP4 inhibitor) and Metformin (a Biguanide). This is an anti-diabetic drug. Type 2 diabetes is a condition in which the body either stops producing enough insulin (the hormone that helps lower blood sugar levels) or develops insulin resistance. As a result, insulin is produced in large quantities but has no effect on the organs.
Sitagliptin is an inhibitor of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) enzyme. It functions by increasing the levels of certain naturally occurring chemicals that reduce high blood sugar levels. Yet another pharmaceutical Metformin belongs to the class of medications known as biguanides. It decreases glucose synthesis in the liver, delays glucose absorption from the intestines, and increases insulin sensitivity in the body. It prevents blood glucose levels from rising to dangerously high levels after meals when taken in combination.
To prevent stomach upset, take Istamet 50 mg/500 mg with food. It is important to take Istamet 50 mg/500 mg at the same time every day. Your physician will determine the appropriate dose, which may change periodically depending on your condition. Hypoglycemia (low blood glucose) is the most frequently reported adverse event associated with Istamet 50 mg/500 mg. Among the symptoms are vertigo, perspiration, palpitations, hunger pangs, and dry mouth and skin. To avoid hypoglycemia, you should avoid skipping meals and carry sugar with you at all times. Moreover, changes in taste, nausea, diarrhea, stomach pain, headaches, and upper respiratory issues may occur.
Your blood sugar level will continue to fluctuate if you stop taking Istamet 50 mg/500 mg without first consulting a physician. Your blood sugar levels may rise if you abruptly stop taking Istamet 50 mg/500 mg, increasing your risk of vision loss (retinopathy), kidney damage (nephropathy), and nerve damage (neuropathy). Avoid Istamet 50 mg/500 mg if you have diabetes type 1, significant kidney disease, or liver disease. Notify your doctor if you have cardiac disease, are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, or are nursing.
Istamet 50 mg/500 mg Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Medicinal Advantages
Istamet 50 mg/500 mg stimulates the pancreas to produce more insulin, enhances insulin utilization, and reduces liver sugar production. It helps to control the rise in blood sugar following a meal. In addition, chronic use does not lead to weight gain. Istamet 50 mg/500 mg is essential for blood sugar control and the prevention of major diabetes-related complications, including vision loss (retinopathy), kidney damage (nephropathy), nerve damage (neuropathy), diabetic foot ulcers, and delayed wound healing.
Use Instructions
Istamet 50 mg/500 mg should not be taken unless prescribed by a physician. Always take Istamet 50 mg/500 mg exactly as your doctor has prescribed. Based on your medical condition, your doctor will determine the frequency with which you should take your medications. With a full glass of water, the tablet should be ingested. Tablets can be broken in half if a smaller dose is required.
Storage
Place in a cool, dry area out of direct sunlight.
Adverse Effects of Istamet 50mg/500mg
Each medication has its own list of side effects. During the first few days of treatment with Istamet 50 mg/500 mg in combination with sulfonylurea or insulin, you may experience low blood sugar, runny nose, sore throat, upper lung infection, diarrhoea, nausea and vomiting, gas, stomach upset, indigestion, general weakness, and headache. However, they would be temporary and could be alleviated after a while. Consult a physician if you continue to experience difficulty. Lactic acidosis (an abnormally high level of lactic acid in the blood) is a rare but potentially fatal adverse effect that can lead to death.
Adverse Drug Reactions
Metformin and sitagliptin are contraindicated in diabetic ketoacidosis and type 1 diabetes. Certain diabetic patients using Metformin and Sitagliptin may develop lactic acidosis, a rare but fatal complication. This disease is characterized by an excess of lactic acid in the blood, which can impair the function of your liver and kidneys, which are responsible for eliminating excess lactic acid from the blood. Inform your doctor if you have ever had pancreatitis (pancreatic inflammation), kidney problems, or a low vitamin B12 level before beginning Metformin and Sitagliptin. When combined with insulin, metformin and sitagliptin may cause hypoglycemia, or dangerously low blood sugar levels. In this scenario, your physician may decrease the dosage of insulin, Metformin, or Sitagliptin. Because prolonged use of Metformin and Sitagliptin may reduce thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), annual TSH testing is advised. In rare cases, you may also develop bullous pemphigoid, a severe skin reaction that requires immediate medical attention. Inform your physician if you are scheduled for a diagnostic procedure requiring the injection of a dye or X-ray contrast agent. Before undergoing an X-ray procedure, Metformin and Sitagliptin should be discontinued for a brief period of time.
Interactions Between Drugs
Antidepressants (bupropion), glaucoma medications, antibiotics (cephalexin, ciprofloxacin), anti-acidity medications (cimetidine), anti-HIV medications (dolutegravir), ethanol, saliva-thinning medications (glycopyrrolate), iodinated X-ray contrast agents, and anti-epileptic medications (topiramate, lamotrigine) interact with Istamet (ranolazine). Other medications, such as sex hormones (androgens), antioxidants (alpha-lipoic acid), pain relievers (aspirin), anti-tuberculosis drugs (prothionamide), growth hormones (pegvisomant), and other antidiabetic drugs, may also increase the risk of low blood sugar.
Drug-Food Interaction: Excessive alcohol consumption may increase the risk of developing Lactic Acidosis, a potentially fatal disease. Therefore, alcoholic beverages should be avoided while taking Istamet.
Metformin and Sitagliptin should be avoided by those with a history of cardiac disease (such as congestive heart failure or myocardial infarction), Vitamin B12 deficiency, or alcoholism.
Safety Recommendations
ALCOHOL
It is prudent to abstain from alcohol while taking medication.
PREGNANCY
Please consult your doctor prior to taking Metformin or Sitagliptin.
FEEDING OF THE BREAST
Please consult your doctor prior to taking Metformin or Sitagliptin.
DRIVING
Drive only if you are mentally and physically stable. If you experience drowsiness as a side effect of these medications, you should not drive or operate heavy machinery.
LIVER
Consult a physician before using this medication if you have a history of or symptoms of liver disease.
KIDNEY
Prior to using the medication, you should consult your doctor if you have a history of or symptoms of kidney disease.
No Habit Development
Advice on Diet and Lifestyle
You should fill half your plate with starchy vegetables, a quarter with protein, and a quarter with whole grains.
Consume food at consistent intervals. Do not wait a considerable amount of time between meals and snacks.
Monitor your blood sugar regularly, especially if there are significant fluctuations.
Commit to at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 1 hour and 15 minutes of vigorous physical activity per week.
To maintain a healthy body mass index, weight reduction must be gradual (18.5 to 24.9).
Replace refined carbohydrate foods with whole grain foods and increase your consumption of fruits, vegetables, and other fiber-rich foods.
Reduce your consumption of foods containing saturated fat (or hidden fat), such as chips, crisps, pastries, cookies, and samosas. Choose omega 3 fatty acid-rich oils for everyday cooking. For frying, utilize palm oil, mustard oil, groundnut oil, rice bran oil, or safflower oil.
Stress can lead to an increase in blood sugar levels. Implementing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, enables you to regulate blood sugar fluctuations caused by stress.
Prioritize the acquisition of low-fat dairy products (low-fat yoghurt, fat-free milk, and cheese, etc.).
Maintain a normal blood pressure as much as possible (140/90). Because it reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease in diabetic individuals.
In addition, this item cannot be returned.
Concern for Patients
Type 2 diabetes is a condition in which the body cannot produce enough insulin or the insulin it does produce does not act correctly or is not utilized properly by the body. This can lead to elevated blood glucose levels (hyperglycaemia). Type 2 diabetes is characterized by an increase in thirst, nighttime urination, poor wound healing, an increase in appetite, fatigue, and blurred vision. In rare instances, weight loss may occur, whereas weight gain is possible under certain conditions. Neuropathy (nerve damage), nephropathy (kidney damage), retinopathy (damaged retina of the eyes or blindness), amputation of limbs, sexual dysfunction, and an increased risk of heart attack or stroke are complications of type 2 diabetes.
FAQs
Type 2 diabetes is a common form of diabetes in which the body’s natural hormone for lowering blood sugar, insulin, does not function properly. As a result, blood glucose levels rise, and symptoms such as increased urination, thirst, and appetite manifest. Diabetes, if left untreated or inadequately treated, can lead to long-term complications including nerve damage, kidney damage, eye damage, and foot problems, as well as a significantly increased risk of developing heart disease.
Consult a doctor if you experience symptoms such as increased hunger, increased thirst, frequent urination (typically at night), unexplained weight loss, exhaustion, blurred vision, sluggish wound/sore healing, or recurrent infections, as these could indicate type 2 diabetes.
Lactic acidosis is a rare but potentially fatal condition caused by an excessive accumulation of lactic acid in the bloodstream. Metformin plus Sitagliptin may result in lactic acidosis if oxygen is depleted from the cells. The symptoms of lactic acidosis include a burning sensation in the muscles, discomfort in the muscles, rapid breathing, nausea, and stomach pain. Immediately consult your physician if this occurs.
If you sense that your blood sugar is falling and you are becoming weak, consume sugary candies or sugary beverages immediately. It will assist in balancing the blood sugar levels in your body. Therefore, it is wise to carry sugar candies with you.
Avoid excessive alcohol consumption while taking Metformin and Sitagliptin, as it may increase your risk of developing lactic acidosis, a potentially fatal condition (too much of lactic acid in the body).
Metformin and Sitagliptin are used exclusively for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, also known as “non-insulin-dependent diabetes.”




Be the first to review “ISTAMET 50/500 15 Tablets”