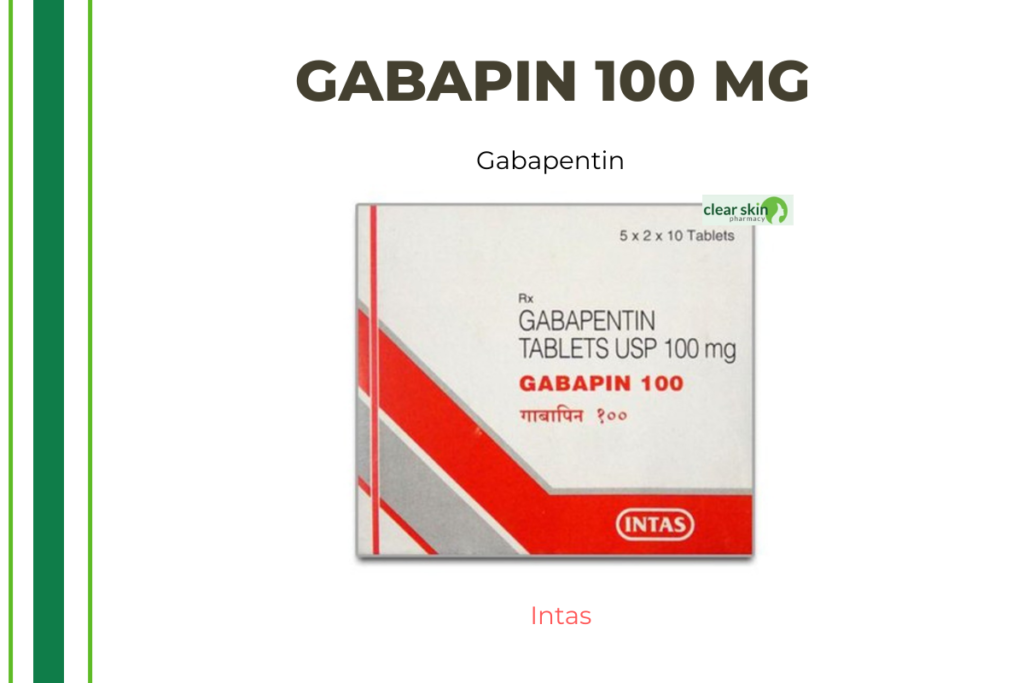
Gabapin 100 mg
Gabapin 100 belongs to the anticonvulsant medication class, which is used to treat or prevent neuropathic pain and epilepsy. In addition, it is occasionally used to alleviate migraine headaches. Neuropathic pain is a form of nerve pain produced by a gradual, chronic nerve disease. Epilepsy, on the other hand, is a condition of the neurological system caused by aberrant brain nerve cell activity.
Gabapin 100 includes Gabapentin, which decreases the risk of seizures and relieves nerve pain by binding to a particular site on voltage-gated calcium channels. Additionally, it decreases the quantity of pain signals emitted by wounded neurons throughout the body.
Gabapin 100 is only available with a valid prescription. It is available as capsules, pills, and a liquid that may be consumed. Gabapin 100 is appropriate for adults and children older than 6 years. Gabapin 100 should be administered precisely as directed. Please do not exceed the recommended dosage or administration frequency. You may experience drowsiness, fatigue, or vertigo as a result of the medicine. The majority of these side effects do not require medical intervention and will disappear with time. However, if you have these side effects frequently, you should visit your physician.
Continue taking Gabapin 100 for as long as prescribed by your doctor to properly treat your condition. Please do not discontinue Gabapin 100 without consulting your doctor first. Withdrawal symptoms are possible. If you are pregnant or nursing, you should not use Gabapin 100 without your doctor’s approval. Gabapin 100 can cause drowsiness or vertigo, therefore only operate a vehicle if you are alert. Children should only have Gabapin 100 with a doctor’s prescription. If you combine Gabapin 100 and alcohol, you may feel increased dizziness and fatigue. To rule out any adverse effects, keep your doctor informed about your current health status and medications.
Gabapin 100 is utilized for the treatment of neuropathy, epilepsy, and migraines.
Medicinal Advantages
Gabapin 100 is an anticonvulsant used to treat neuropathic pain (nerve damage-related pain), fibromyalgia (musculoskeletal pain), and epilepsy (fits). By binding to a specific site on voltage-gated calcium channels and limiting the action of overexcited channels, it alleviates nerve pain and lowers the risk of seizures. It reduces nerve pain by interfering with pain signals delivered from damaged nerves to the brain.
Use Instructions
Gabapin 100 mg may be used with or without meals. It is forbidden to chew, crush, or break the pill. With a glass of water, ingest it in its whole. Gabapin 100 should only be used if prescribed by a physician. Your physician will determine how long you must take Gabapin 100 based on your medical condition.
Place in a cool, dry area out of direct sunlight.
Side Effects
Gabapin 100, like many other medications, has certain adverse effects, although not everyone will experience them. Common side effects of Gabapin 100 include drowsiness, fatigue, or vertigo, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, contracting more infections than normal, mood changes, swelling of the arms and legs, blurred vision, dry mouth, erectile dysfunction in men, weight gain, appetite, memory problems, and headaches. The majority of adverse effects of Gabapin 100 do not require medical treatment and diminish over time. However, if the bad effects persist, see a physician.
Drug Recommendations
If you have an allergy to any of the substances in Gabapentin, you should not take the medication. Inform your physician if you have indications of suicidal ideation or behavior, drug addiction, chronic pulmonary insufficiency, muscular weakness, cardiac issues, or liver/kidney damage prior to using Gabapentin. Please do not discontinue Gabapentin without consulting your physician first. Withdrawal symptoms are possible. If you are pregnant or nursing, you should not use Gabapentin without your doctor’s approval. Avoid driving and consuming alcoholic beverages while taking Gabapentin, since it may induce dizziness and fatigue. Consult your doctor immediately if you have suicidal thoughts. If you combine Gabapentin with St. John’s Wort (an antidepressant) herbal supplement, you may have increased dizziness and fatigue. To rule out any adverse effects, keep your doctor informed about your current health status and medications.
Interactions Between Drugs
Gabapentin may interact with analgesics (morphine, hydrocodone, oxycodone, tramadol, codeine), antidepressants (fluoxetine, amitriptyline), antipsychotics (quetiapine), antimalarials (mefloquine), a weight-loss medication (orlistat), antihistamines, and other drugs (diphenhydramine, cetirizine).
Alcohol and the herbal supplement St. John’s Wort (an antidepressant) should be avoided when taking Gabapentin since they may worsen dizziness and fatigue.
Gabapentin may interact with drugs used to treat heart conditions, depression, diabetes, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, suicidal thoughts, and kidney and liver disorders.
Safety Suggestions
ALCOHOL
Alcohol intake is risky since it might aggravate adverse effects including dizziness and fatigue.
PREGNANCY
Gabapentin is a category B1 medicine for use during pregnancy. Please consult with a physician. Before prescribing Gabapentin, your physician will evaluate its advantages and risks.
BREAST FEEDING
Gabapentin is generally compatible with breastfeeding. Before using Gabapentin, see your physician. Before prescribing Gabapentin, your physician will evaluate its advantages and risks.
DRIVING
Do not drive or operate machinery if you experience dizziness or sleepiness while taking Gabapentin. Gabapentin can also create blurred or double vision; thus, you should not drive if you are taking it. If the symptoms persist after a few days, consult a physician.
LIVER
Gabapentin should be used with care in patients having a history of liver illness or dysfunction. Your physician can adjust the dosage if required.
KIDNEY
Gabapentin should be used with care, particularly if you have or have had renal disease or dysfunction. Your physician can adjust the dosage if required.
Habit formation is possible.
Advice on Diet and Lifestyle
Include foods high in vitamin B and vitamin D in your diet.
Cayenne pepper should be incorporated into your diet since it can reduce neuropathy-related discomfort.
Regular exercise can improve both overall health and pain management.
Get sufficient rest and sleep.
Take a leisurely bath in warm water.
Avoid tobacco use and alcohol consumption.
Massages with essential oils might enhance circulation.
Through the stimulation of pressure points, acupuncture can be therapeutic.
Meditation and yoga can help reduce stress, decrease pain sensitivity, and enhance coping abilities.
Recommendations
It is not recommended to use Gabapentin for a lengthy period of time, since it may lead to mental or physical dependence.
If you are taking antacids containing aluminum or magnesium, you must wait at least 2 hours between taking Gabapentin and taking these antacids to avoid a medication interaction.
Because Gabapentin might produce dizziness or drowsiness, rise slowly from a sitting or lying posture.
If Gabapentin causes dry mouth, drink water or other liquids, consume hard candies or ice, chew (sugarless) gum, or use a saliva replacement.
Additional Information : This item is non-refundable.
Concerns of Patients
Neuropathic pain is a neurological disorder resulting from nerve damage caused by chronic degenerative nerve disease, amputation, diabetes, infection, or trauma. The pain may be prickling, stabbing, tingling, or burning, and it may be intermittent or continuous. In addition to numbness and loss of feeling, neuropathic pain is frequently accompanied with a lack of sensation. Typically, the body communicates pain signals in response to an injury, but it also transmits pain signals in response to neuropathic pain, which is pain that is not caused by an injury. Symptoms include unexpected pain, an unpleasant sensation, shooting, scorching, or stabbing pain, trouble relaxing or sleeping, and discomfort caused by ordinarily painless occurrences.
Epilepsy is a disorder characterized by a rapid electrical spike in the brain. It is a condition of the neurological system caused by the disruption of nerve cell activity in the brain. Generalized and partial seizures are the two forms of seizures. Generalized seizures impact the whole brain, whereas partial seizures affect only a segment of the brain. Muscular twitches and spasms that cannot be controlled are frequent adverse effects of seizures. People who experience stronger seizures may become disoriented or unconscious. Possible causes include high temperature, trauma, hereditary disease, brain damage, and stroke.
FAQs
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant. It functions to prevent epileptic seizures by reducing abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It inhibits pain by interfering with pain signals as they travel from the brain to the spine.
Consuming alcohol is risky since it might worsen adverse effects such as dizziness and drowsiness.
Do not drive or operate machinery if you experience dizziness or sleepiness while taking Gabapentin. Gabapentin can also create blurred or double vision; thus, you should not drive if you are taking it. If the symptoms persist after a few days, consult a physician.
Long-term Gabapentin users frequently experience dizziness, blurred vision, weight gain, fatigue, difficulties concentrating, hand and foot swelling, and dry mouth.
Gabapentin might induce weight gain because it stimulates appetite. On the other hand, regular physical exercise and a balanced diet rich in low-calorie foods may help you maintain a healthy weight. Please consult your physician if you have any more concerns about maintaining a healthy weight.
Some long-term users of gabapentin have developed an addiction to the medication. If this occurs, you will have withdrawal symptoms if you discontinue the medication. Consult your physician if you are concerned about becoming physically reliant on gabapentin.






Be the first to review “GABAPIN 100 MG 15 Tablets”